Anesthesia Monitoring During Surgery: The Critical Role of BIS in Patient Monitors
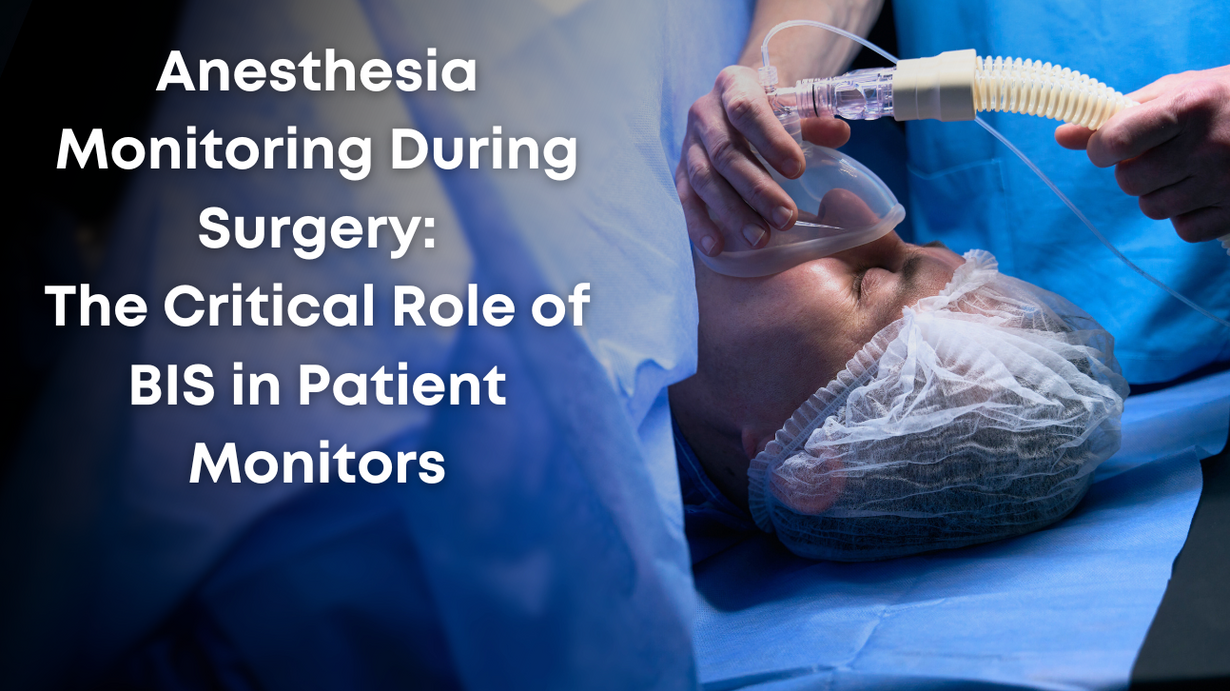
Anesthesia monitoring during surgery is a critical component of ensuring patient safety and successful surgical outcomes. Among the various parameters monitored, the Bispectral Index (BIS) has emerged as a pivotal tool in assessing the depth of anesthesia. This blog explores the fundamentals of anesthesia monitoring, delves into the significance of BIS in patient monitors, and underscores its impact on clinical practice.
The Fundamentals of Anesthesia Monitoring
Anesthesia is a complex medical procedure that requires precise monitoring to maintain the balance between sufficient anesthesia and patient safety. Anesthesia monitoring encompasses the continuous assessment of the patient's physiological state, including vital signs, anesthetic depth, and overall well-being. Key parameters include:
Heart Rate and Rhythm: Monitoring the heart rate and rhythm is essential to detect any abnormalities such as arrhythmias that may arise during surgery. Electrocardiography (ECG) is commonly used for this purpose.Blood Pressure: Blood pressure monitoring ensures that the patient maintains stable hemodynamics. Both invasive and non-invasive methods can be used, depending on the surgery's complexity.
Oxygenation and Ventilation: Pulse oximetry and capnography are employed to monitor oxygen saturation and carbon dioxide levels, respectively. These parameters help ensure adequate oxygen delivery and ventilation.
Temperature: Maintaining the patient's body temperature within a normal range is crucial to prevent hypothermia or hyperthermia, which can lead to complications.
Neuromuscular Function: For surgeries involving muscle relaxation, monitoring neuromuscular function helps adjust the administration of muscle relaxants.
Depth of Anesthesia: Assessing the depth of anesthesia is vital to avoid both under- and over-sedation. This is where the Bispectral Index (BIS) becomes particularly significant.
Understanding Bispectral Index (BIS)
The Bispectral Index (BIS) is a numerical value derived from the electroencephalogram (EEG) that provides a measure of the patient's level of consciousness during anesthesia. Developed in the 1990s, BIS has revolutionized the way anesthesiologists monitor and manage anesthesia depth.
How BIS Works
BIS monitoring involves placing electrodes on the patient's forehead to measure brain wave activity. The EEG data is then processed using proprietary algorithms to generate a single BIS value, typically ranging from 0 to 100. This value correlates with the patient's level of consciousness:
- 100: Fully awake and alert
- 70-90: Sedated but responsive
- 60-70: Moderate anesthesia, adequate for most surgical procedures
- 40-60: Deep anesthesia, suitable for major surgeries
- 0-40: Unconscious, typically indicative of general anesthesia
The Importance of BIS in Anesthesia Monitoring
BIS monitoring offers several advantages that enhance patient safety and optimize anesthesia management:
Preventing Awareness During Surgery: One of the primary concerns in anesthesia is the risk of intraoperative awareness, where a patient becomes conscious during surgery but is unable to move or communicate. BIS helps reduce this risk by providing real-time feedback on the patient's level of consciousness, allowing anesthesiologists to adjust anesthesia levels accordingly.Optimizing Anesthetic Dosing: Over-sedation can lead to prolonged recovery times and increased risk of complications, while under-sedation can result in patient discomfort and awareness. BIS enables precise titration of anaesthetic agents, ensuring that the patient remains adequately sedated without excessive dosing.
Improving Recovery Times: By maintaining optimal anesthesia levels, BIS monitoring contributes to faster recovery times and reduces the incidence of postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD). This is particularly important for elderly patients and those with pre-existing cognitive impairments.
Enhancing Patient Safety: BIS monitoring enhances overall patient safety by providing a continuous and objective assessment of anesthesia depth. This allows for early detection of potential issues and timely intervention, reducing the likelihood of adverse events.
Cost-Effectiveness: Although the initial cost of BIS monitoring equipment may be higher, the long-term benefits in terms of improved patient outcomes, reduced complications, and shorter hospital stays make it a cost-effective solution.
Clinical Applications of BIS Monitoring
BIS monitoring is utilized across a wide range of surgical procedures and patient populations. Some notable applications include:
Cardiac Surgery: In cardiac surgery, maintaining a stable depth of anesthesia is critical due to the intricate nature of the procedures and the patient's hemodynamic status. BIS monitoring helps achieve this balance, reducing the risk of awareness and hemodynamic instability.Neurosurgery: Neurosurgical procedures often require precise control of anesthesia to avoid interfering with neurological assessments. BIS monitoring aids in maintaining an appropriate level of sedation while allowing for intraoperative neurological evaluations.
Pediatric Surgery: Children are particularly vulnerable to the effects of anesthesia, making accurate monitoring crucial. BIS provides an objective measure of anesthesia depth, ensuring that pediatric patients receive appropriate sedation.
Obstetric Surgery: In obstetric surgery, maintaining maternal and fetal well-being is paramount. BIS monitoring helps balance the depth of anesthesia, ensuring maternal comfort while minimizing fetal exposure to anesthetic agents.
Emergency and Trauma Surgery: In emergency and trauma situations, rapid and accurate assessment of anesthesia depth is essential. BIS monitoring provides real-time data, allowing for swift adjustments to anesthesia levels.
Challenges and Considerations in BIS Monitoring
While BIS monitoring offers significant advantages, there are some challenges and considerations to be aware of:
Interference and Artifacts: BIS values can be affected by electrical interference, muscle activity, and other artifacts. Proper electrode placement and signal quality assessment are crucial to obtaining accurate readings.Individual Variability: BIS values may vary among individuals due to factors such as age, medication use, and underlying medical conditions. Anesthesiologists must consider these variations when interpreting BIS data.
Supplemental Monitoring: BIS should be used in conjunction with other monitoring modalities, such as clinical observation and traditional vital signs. It provides valuable information but should not be the sole determinant of anesthesia management.
Training and Familiarity: Effective use of BIS monitoring requires proper training and familiarity with the technology. Anesthesiologists and healthcare providers must be well-versed in interpreting BIS values and integrating them into clinical practice.
Future Directions in Anesthesia Monitoring
As technology continues to advance, the field of anesthesia monitoring is poised for further innovations. Some potential future directions include:
Improved Algorithms: Ongoing research aims to refine BIS algorithms to enhance accuracy and reduce susceptibility to artifacts. This could lead to even more precise assessment of anesthesia depth.Integration with Other Monitoring Systems: Combining BIS with other monitoring modalities, such as hemodynamic monitoring and neuromuscular assessment, could provide a comprehensive view of the patient's physiological state.
Wearable and Wireless Monitoring: The development of wearable and wireless monitoring devices may enable continuous assessment of anesthesia depth in diverse clinical settings, including ambulatory and remote surgeries.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms could enhance the interpretation of BIS data, leading to more personalized and adaptive anesthesia management.
Closed Loop Anesthesia Delivery Systems (CLADS): A significant advancement in anesthesia technology is the development of Closed Loop Anesthesia Delivery Systems (CLADS) by Clarity Medical in collaboration with PGIMER. CLADS uses real-time data, including BIS values, to automatically adjust the delivery of anesthetic agents. This system ensures precise control of anesthesia depth, minimizes human error, and enhances patient safety. By continuously monitoring and adjusting anesthesia levels, CLADS aims to optimize patient outcomes and streamline anesthesia management in various surgical settings.
Conclusion
Anesthesia monitoring during surgery is a critical aspect of ensuring patient safety and optimal surgical outcomes. The Bispectral Index (BIS) has emerged as a valuable tool in assessing the depth of anesthesia, offering numerous benefits such as preventing intraoperative awareness, optimizing anesthetic dosing, improving recovery times, enhancing patient safety, and providing cost-effectiveness. While challenges and considerations exist, the integration of BIS into clinical practice represents a significant advancement in anesthesia management. As technology continues to evolve, the future of anesthesia monitoring holds promise for even greater precision and patient care.