A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Preventing Herniated Disks
Our modern lifestyle is very different from what our bodies evolved for. Today, many of us spend more hours sitting or peering at our mobile phones than being up and about. However, long hours at the desk can lead to several health problems, including back and neck pain. Although you can address pain to some extent through chairs with neck and lumbar support, this problem can sometimes lead to a herniated or slipped disk.
What are the most common reasons for back pain?
Back pain can have many different causes, some of which include:
- > Muscle or ligament strain: This is one of the most common causes of back pain, often caused by overuse or poor posture.
- > Bulging or ruptured (herniated) disks: These can occur when the soft material inside a spinal disk pushes out through a tear or rupture in the outer layer.
- > Arthritis: This condition can cause inflammation in the joints of the spine, leading to back pain.
- > Osteoporosis: This condition weakens the bones, making them more susceptible to fractures and compression fractures in the spine.
- > Spinal stenosis: This condition involves a narrowing of the spaces within the spine, which can put pressure on the nerves and cause pain.
- > Scoliosis: This is a condition in which the spine curves to the side, often causing back pain.
- > Infections or tumors: In rare cases, infections or tumors can cause back pain.
- > Poor posture: Sitting or standing in a slouched or hunched position can put strain on the muscles and ligaments in the back.
- > Repetitive motion: Doing the same movements repeatedly, such as bending or twisting, can cause strain on the back.
- > Stress: Emotional stress can cause muscle tension in the back, leading to pain.
If you are experiencing back pain, seeking medical attention is important to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
What is a herniated disk?
A herniated disk, also known as a slipped or ruptured disk, occurs when the soft tissue inside a spinal disk protrudes through a tear in the outer layer. This can lead to pain, numbness, and weakness in various body parts.
What are the symptoms of a herniated disk?
Although the symptoms of a herniated disk may vary across individuals, some common tell-tale signs suggest you may have a herniated disk:
- > Pain in the neck, lower back, or legs
- > Numbness or tingling in the arms, legs, or buttocks
- > Weakness in the muscles of the affected area
- > Loss of bladder or bowel control (in severe cases)
How diagnose a herniated disk?
Most healthcare professionals use a combination of methods to diagnose a herniated disk. They can use imaging techniques such as CT Scans, X-Rays or an MRI to diagnose the issue at hand or use a combination of imaging, physical examination, and EMG or Electromyography to diagnose a herniated disk.
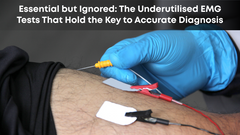
What is EMG or Electromyography?
Electromyography is a diagnostic technique that measures the electrical activity of muscles and nerves. Electrodes record the electrical activity of the muscle while it is at rest and during contraction. The electrical activity is then displayed on a screen or recorded for analysis. An EMG test can help diagnose nerve and muscle disorders, including herniated disks and other conditions that cause back pain.
The test may also include nerve conduction studies (NCS), which involve the application of small electrical shocks to a nerve to measure how quickly electrical impulses travel through the nerve. These tests can help identify nerve damage or compression, which a herniated disk or other conditions can cause.
What is the leading cause of a herniated disk?
As with many other diseases, herniated disks do not have a specific cause. Here's a list of causal factors that can lead to a herniated disk:
- > Modern lifestyles, such as excessive sitting and bad posture
- > Age-related wear and tear of the spinal disks
- > Improper lifting technique or repetitive strenuous activities that put pressure on the back
- > Trauma or injury to the back
- > Genetics or family history of herniated disks
- > Being overweight or having poor posture
How can disk herniation be prevented?
Prevention is better than cure. There are many ways to ensure that you do not strain your back and cause excessive trauma that leads to a herniated disk. Some of these include:
- > Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce strain on the back
- > Using proper lifting techniques when lifting heavy objects
- > Regular exercise to strengthen the muscles that support the back
- > Maintaining a good posture while sitting or standing
- > Taking frequent breaks when sitting for long periods
- > Avoiding repetitive movements or activities that strain the back
If you experience symptoms of a herniated disk, it's essential to seek medical attention. Treatment may include physical therapy, pain management, or surgery in severe cases. You can sometimes manage the condition with conservative treatments such as rest, ice or heat therapy, and over-the-counter pain relievers.
How can Clarity Medical help?
Clarity Medical's EasyTrace is world’s smallest EMG/NCS/EP machines available today. Powered by USB, this device does not need an external power supply and can easily perform 17 distinct diagnostic tests. Test files can be saved in various formats for ease of reference and review, and the ultra-compact size helps medical professionals to conduct these tests anywhere.
A highly intuitive, easy-to-use interface and super convenient controls make EasyTrace the first choice for EMG/NCS/EP diagnostics. The machine has colour-coded buttons for ease of access and optimal handling during an examination or patient evaluation. The robust shock stim handle makes EasyTrace extremely easy to operate, and its ultra-compact size makes it suitable for emergency usage anywhere.